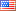
| Amount | Ingredient | $ / day | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.78 | g | L-Histidine | $0.07 | Amazon |
| 1.54 | g | L-Isoleucine | $0.08 | Amazon |
| 3 | g | L-Leucine | $0.19 | Amazon |
| 2.31 | g | L-Lysine | $0.06 | Amazon |
| 0.8 | g | L-Methionine | $0.05 | Amazon |
| 0.316 | g | L-Cysteine | $0.01 | Amazon |
| 1.54 | g | L-Phenylalanine | $0.05 | Amazon |
| 0.385 | g | L-Tyrosine | $0.02 | Amazon |
| 1.155 | g | L-Threonine | $0.03 | Amazon |
| 0.308 | g | L-Tryptophan | $0.03 | Amazon |
| 2 | g | L-Valine | $0.06 | Amazon |
| 6 | g | L-Glutamate | $0.20 | Amazon |
| 1 | g | Glycine | $0.03 | Amazon |
| 0.1 | g | Vitamin A (Palmitate) | $0.01 | Amazon |
| 0.1 | g | Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0 | g | Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 1 | pill | Vitamin K (K2) | $0.07 | Amazon |
| 0.04 | g | Vitamin E (d-alpha Acetate) | $0.01 | Amazon |
| 0.002 | g | Vitamin B1 (Thiamine HCL) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.002 | g | Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.02 | g | Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.01 | g | Vitamin B5 (Calcium Pantothenate) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.002 | g | Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine HCL) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.003 | g | Vitamin B7 (Biotin 1%) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 1 | pill | Vitamin B9 (5-MTHF) | $0.10 | Amazon |
| 0.001 | g | Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin 1%) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 2.5 | g | Calcium (Carbonate) | $0.07 | Amazon |
| 1.5 | g | Magnesium (Carbonate) | $0.04 | Amazon |
| 0.09 | g | Zinc (Gluconate) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0.5 | pill | Selenium (L-Selenomethionine) | $0.02 | Amazon |
| 0.021 | g | Manganese (Gluconate) | $0.00 | Amazon |
| 0 | g | Iodine (Potassium Iodide) | $0.00 | Bulk Supplements |
| 0.5 | pill | Molybdenum (Amino Acid Chelate) | $0.04 | Amazon |
| 0.25 | pill | Chromium (Chromium Picolinate) | $0.01 | Amazon |
| 10 | g | Potassium (Citrate) | $0.37 | Amazon |
| 1.5 | g | Choline (Bitartrate) | $0.05 | Amazon |
| 50 | g | Ghee | $1.21 | Amazon |
| 15 | g | MCT Oil | $0.37 | Amazon |
| 5 | ml | Fish oil, cod liver | $0.13 | Amazon |
| 5 | ml | Hemp Seed Oil | $0.09 | Amazon |
| 4 | g | Salt (Himalayan Pink) | $0.03 | Amazon |
| 25 | g | Glucose | $0.13 | Amazon |
| 0.5 | pill | Copper (Amino Acid Chelate) | $0.02 | Amazon |
| 0.5 | pill | Iron (Amino Acid Chelate) | $0.04 | Amazon |
| 5 | g | NOW Foods MSM Sulfur Powder | $0.12 | Amazon |
| 3 | g | Monosodium Phosphate | $0.21 | Amazon |
| 5 | ml | Oil, sunflower, linoleic, (approx. 65%) | $0.17 | Amazon |
| 15 | ml | Oil, olive, salad or cooking | $0.23 | Amazon |
| 5 | g | Fructooligosaccharides | $0.16 | Amazon |
Amounts for: Total Daily Cost: | $4.56 | Add Ingredients to Amazon Cart | ||
Description
A recipe designed for a 77kg man based upon the purest compounds available and US DRI and WHO recommendations. Using the most fundamental chemicals limits the possibility of contamination or malabsorption from poor processing and reduces the energy needs of the individual.*
When nutritional information is unavailable, substitutions and corrections are made using mature human breast milk as a framework. Since breast milk coevolved with the human digestive system, it follows that milk is at least a useful tool for ingredient evaluation. Some modifications are necessary (e.g. lactose intolerance) and have been noted.
I do have some misgivings about the vitamin and mineral compounds used. Some were chosen for ease of purchasing and cost and not necessarily for maximum nutrition. Those compounds known to not be absorbed at all (e.g. Magnesium Oxide) were obviously avoided. It might be prudent to reduce concentrations of some ingredients given increased absorption. Potassium should be particularly scrutinized given the possibility of cardiac arrest if incorrectly prepared. Much more evaluation is needed.
A second soylent recipe will be prepared with supplemental compounds. Exogenous "pseudovitamins" have shown some efficacy in various apects of health. For instance, the body produced and consumes approximately two grams of creatine per day but also possesses transporters for absorbing creatine from the diet. Supplemental creatine has great evidence and massive effects on physical and mental performance. Many of these compounds exists and are easily supplemented. Sufficient vitamin status only guarantees average performance by definition. Why be average when you can go above and beyond? Xenobiotics, bioactive compounds not produced in the body and not normally consumed through diet, such as caffeine will not be addressed.
To Do/Incomplete
- Evaluate electrolyte concentrations to reduce gastric distress
- Evaluate vitamin and mineral compounds for competition and absorption properties
- Locate mixtures of ingredients for ease of preparation (such as BCAAs instead of the individual AAs)
- Evaluate vitamin class compounds for single compound effectiveness (e.g. Vitamin E acetate)
- Locate purer forms of fatty acids
- Attach research references
- Evaluate sodium and glucose concentrations for coactive transport concentrations
- Locate acceptable sources of fiber (GOS are a possiblity); feed the gut bacteria
Preparation and Consumption Notes
- Target 88% water by weight
- To be consumed slowly, reducing gastric distress
- Homemade grass-fed ghee cuts cost by $0.70 per day
*Let us take whey protein for example. Whey denatures very easily even at hot water temperatures. Denatured proteins are at the very least more difficult to absorb. Another issue is with contamination. Whey protein concentrate can contain toxins fed to the cows that produced the milk. Aflatoxins are common in mass-produced animal feed and therefore present in some quantities in the whey. Several products are available using grass-fed cows and low temperature processing, but this only increases the quality (and cost). It is easier to use pure amino acids which still have the possibility of contamination, but cannot be denatured by definition. Furthermore, the body expends considerable energy in the breakdown of compounds. Using pure compouds limits this expenditure.